
 JSDAI Introduction
JSDAI Introduction 
Overview of the SDAI management object
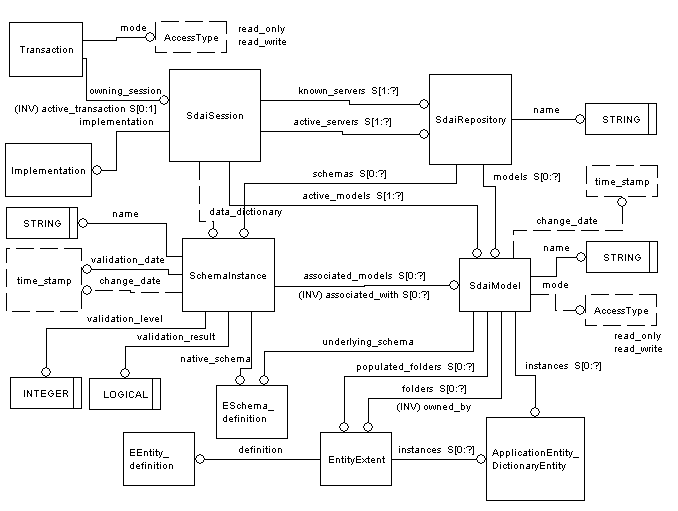
In the previous examples we already learned about
-
SdaiSession, the root from which every SDAI activity starts from
-
Implementation, to provide version and level information of the implementation
-
SdaiTransaction, to control simultaneous updating of changes
-
SdaiRepository, the physical storage container for SchemaInstances and
SdaiModels
-
SdaiModel, to group entity instances based on one express schema
Further management classes are
-
SchemaInstance as a logical grouping of models to define a valid population
of an express schema
-
EntityEntent, an auxiliary class to group entity instances of one entity
data type
-
SdaiException, thrown in case of error conditions
The most important entities of the dictionary schema, needed for late binding
access, are:
-
schema_definition
-
entity_definition
-
attribute

 Copyright 1998, LKSoftWare GmbH
Copyright 1998, LKSoftWare GmbH 

